Background
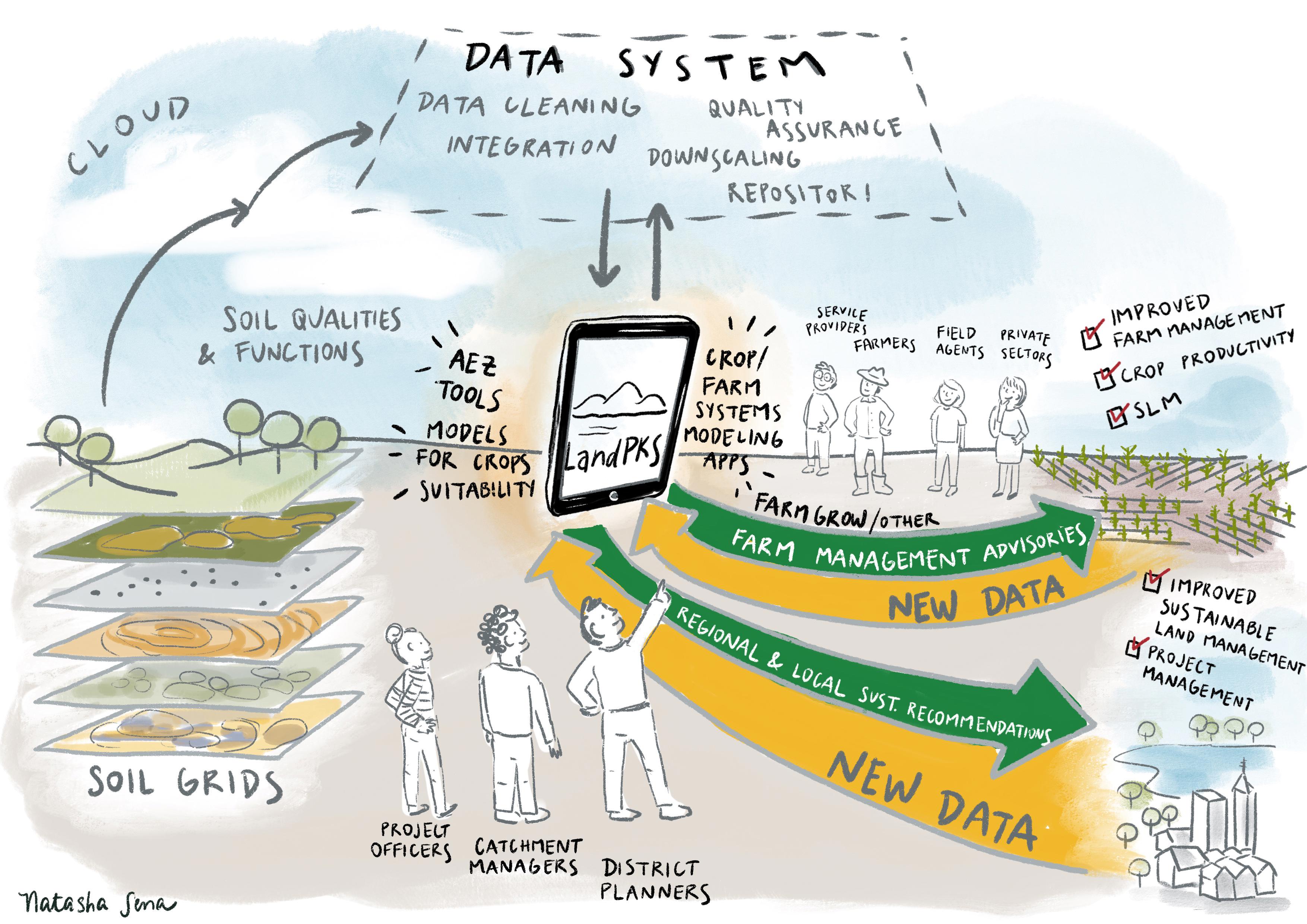
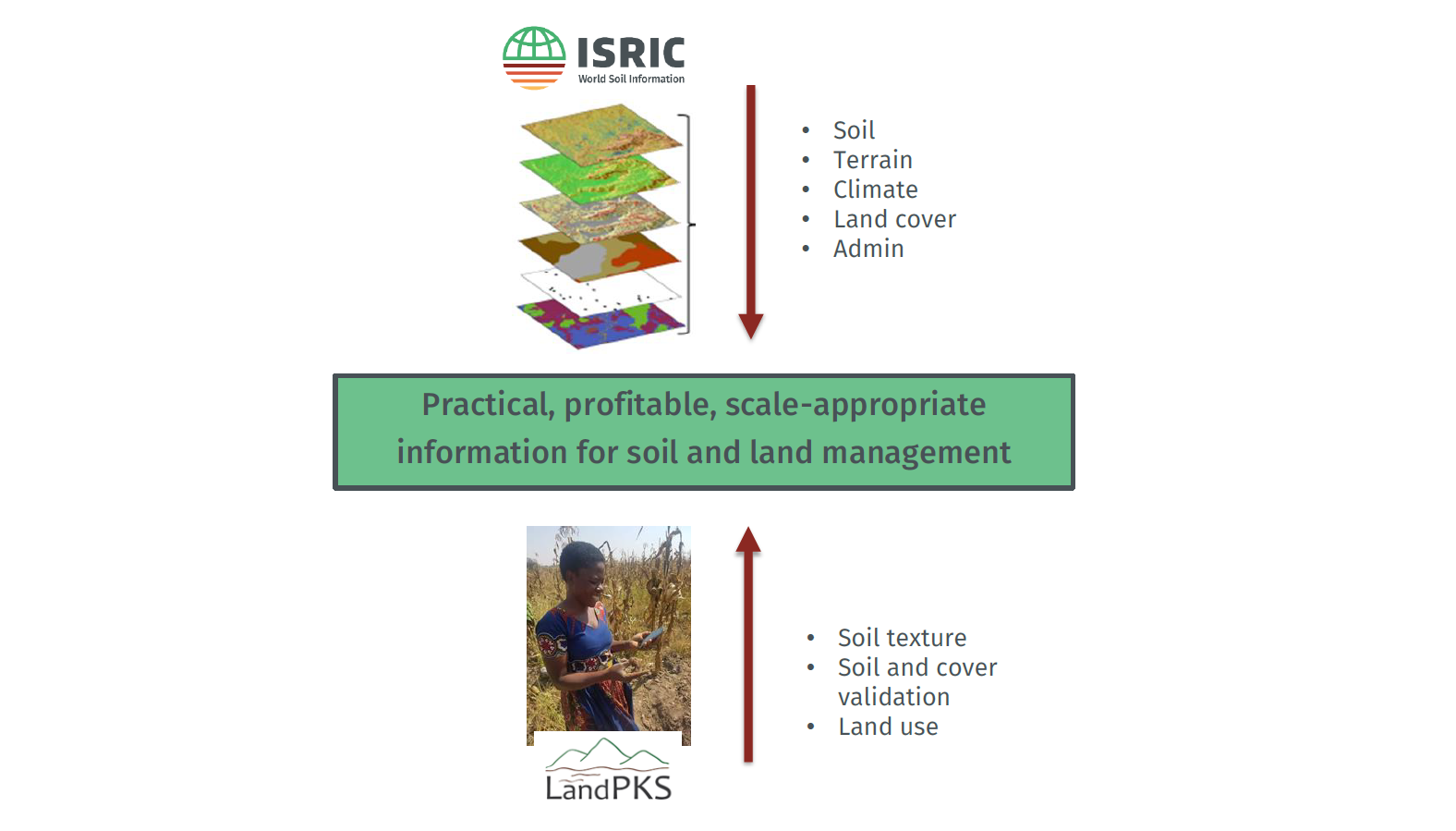
Land Potential Knowledge System (LandPKS) is a knowledge system of open-source tools for land resource planners and managers to collect, share and use soil and land management-related data through a mobile phone app and desktop portal. The United States Department of Agriculture - Agricultural Research Service (USDA-ARS) initiated LandPKS in 2013 with United States Agency of International Development (USAID) funding for use as a monitoring tool for land conservancies, an extensive resource for agricultural development, and a guide for local and regional land planning.
The LandPKS mobile phone app and desktop data portal aim to be the primary access point for free, simple-to-use, and locally appropriate technologies and knowledge needed to make sustainable land management decisions. The program develops innovative web-based and mobile data collection and analysis methods and tools to support local land-use planning. LandPKS helps project managers optimise the design and implementation of food security, land restoration, climate change adaptation, biodiversity conservation programs, and field-level management recommendations.